When you search something on Google, you get a list of links—news sites, blogs, forums, and more—all ranked based on hundreds of SEO factors. But when you ask the same question on ChatGPT, the answer is delivered instantly, without links or ads. So what's happening behind the scenes? How does ChatGPT decide what information to give you? And how is it different from a traditional search engine like Google?
This article explains how ChatGPT handles search queries, the source weightage it gives, and how it's fundamentally different from a search engine like Google.
In simple terms, source weightage refers to how much importance is given to different types of content sources—like government sites, popular news platforms, or individual blogs—when generating a response or ranking a search result.
In Google, this determines which websites appear at the top of search results. In ChatGPT, it influences the type of information included in the response, based on its training data and internal knowledge base.
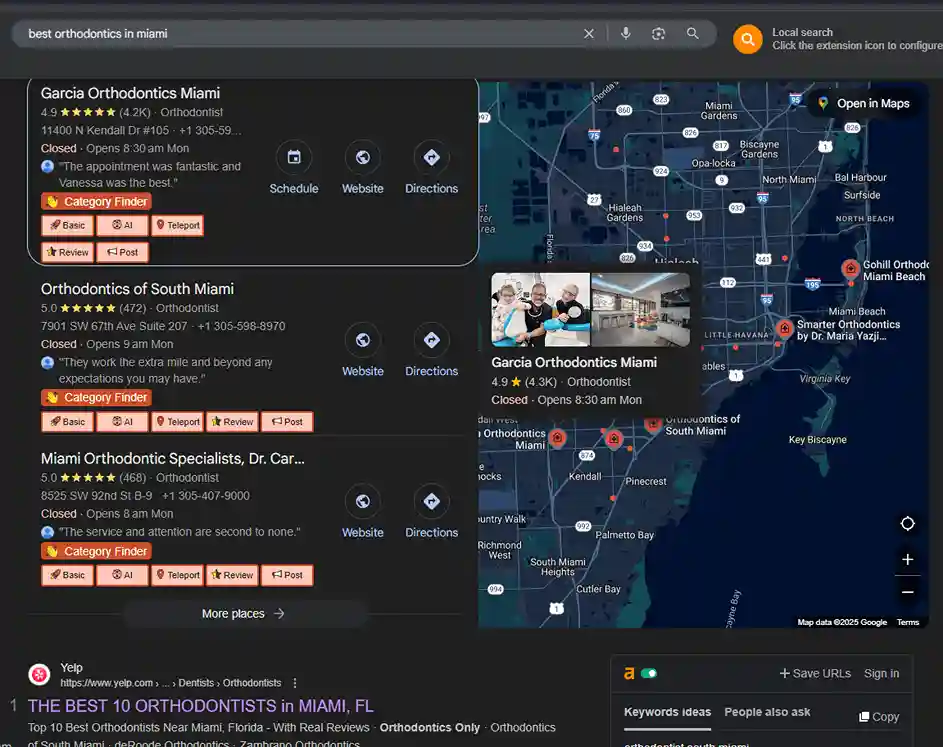
Google is a real-time search engine that crawls and indexes billions of web pages across the internet. When a user types a query—like "best orthodontics in Miami"—Google rapidly analyzes it and returns the most relevant web pages based on hundreds of ranking signals.
Google generates results based on a combination of:
- Real-time web crawling and indexing Google constantly scans websites, updates its index, and uses it to pull fresh content instantly.
- Ranking algorithms and SEO signals Factors like backlinks, domain authority, keyword relevance, mobile usability, page speed, and more determine which pages rank highest.
- User behavior and intent modeling Click-through rates, bounce rates, and historical behavior help Google fine-tune what users are most likely looking for.
- Local and personalized signals Google considers your location, device type, and past searches to tailor results—especially for local or service-based queries.
Google's search results include:
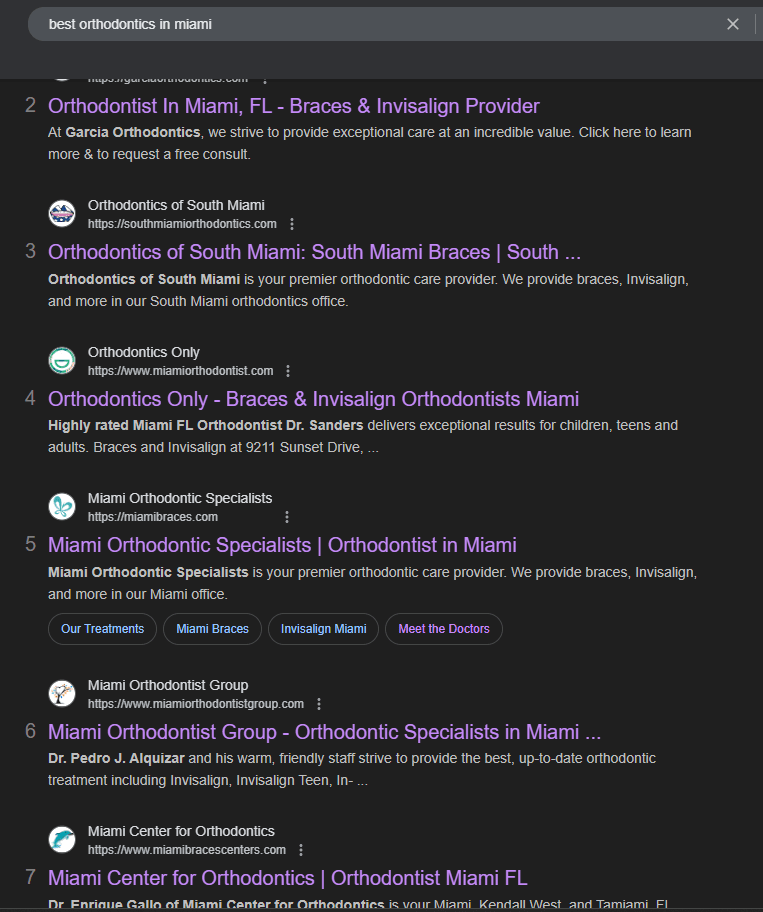
- Blue link listings to websites
- Ads and sponsored placements
- Featured snippets, maps, FAQs, videos, and knowledge panels
- Verified business profiles with reviews, hours, and directions
Google Business Results:
Websites Results:
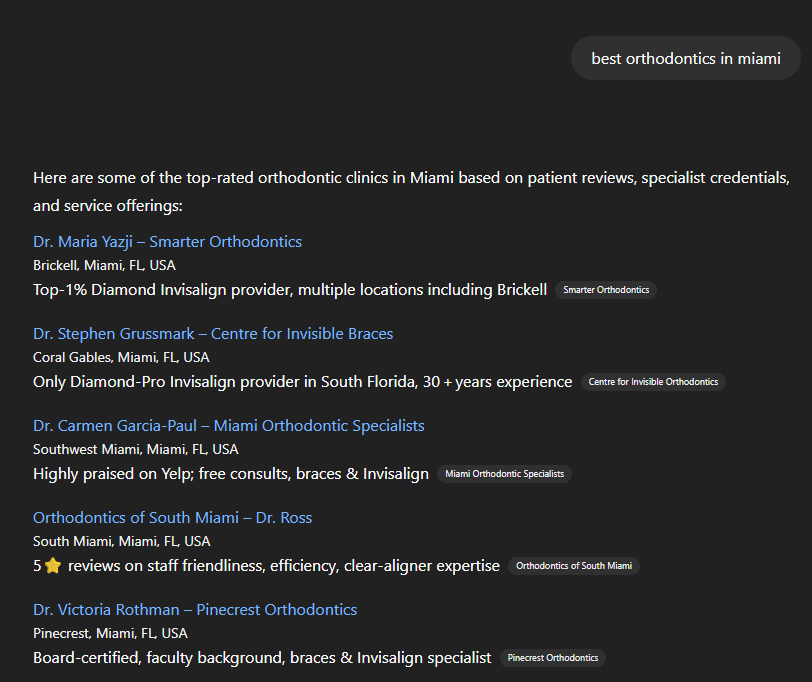
ChatGPT does not search the internet in real-time (unless connected to live web tools). Instead, it generates answers based on a mixture of:
- Pre-trained data (books, websites, articles, documentation, etc. up to its knowledge cutoff)
- Patterns in language and factual correlations learned during training
- Optional live data plugins (for Pro users or web-enabled tools)
It doesn't rank links or show sources unless asked explicitly. Instead, it synthesizes answers that represent the most likely, useful, and accurate information based on how it was trained.
| Source Type | Weightage (%) | Use Case / Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| Structured Directories (Yelp, Zocdoc, Healthgrades, Avvo, etc.) | 25–35% | Local service queries, "best X in city", where review count + ratings matter |
| Business Listings (GBP, Bing Places) | 10–20% | Often overlooked unless the business is highly reviewed or linked elsewhere |
| Official Websites / Homepages | 15–25% | Pulled when brand-name is searched or the site has high authority |
| Aggregators & Comparison Sites (e.g., Forbes, CNET) | 10–15% | For ranking-style queries like "Top 10 X" or "Which is better: A vs B" |
| Reddit / Forums / Quora | 10–15% | When personal opinions or lived experience are likely relevant |
| News & Media (NYT, Local News, etc.) | 5–10% | For trending or reputation-sensitive businesses or medical controversies |
| Blogs / Niche Sites / SEO content | 5–10% | Lower unless they have backlinks or are referenced across platforms |
| Social Media Profiles (Facebook, Instagram) | <5% | Rarely cited directly, but considered for verification or sentiment |
- Query Type:
- "Which is the best?" → pulls from reviews and comparisons (Yelp, forums)
- "Cost of X?" → tends to favor directories and official sites
- "What's the difference between A and B?" → leans more on educational and editorial content (blogs, Wikipedia, etc.)
- Source Recency (for live searches only): Newer pages are preferred only if they're from reliable sites (e.g., not just any blog post).
- Cross-Verification: ChatGPT favors sources cited by multiple other pages or domains. E.g., if Yelp, Reddit, and a blog all mention the same practice favorably, it gets a boost.
- Schema & Structured Data: Pages with valid schema markup (e.g., LocalBusiness, FAQ, Review) are more likely to be parsed accurately and prioritized.
- Query Interpretation → Is it factual, comparative, local, or opinion-driven?
- Search Execution via Bing API (if live) → Top ~20 results are fetched.
- Internal Ranking of Pages → Relevance score + confidence score + cross-source validation.
- Summary Generation → High-confidence snippets used to build a natural language summary. Sources weighted accordingly.

| Feature | Google Search | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time Web Access | Yes | No (unless web tools are enabled) |
| Source Ranking | Yes, based on SEO & backlinks | No, uses internal knowledge weighting |
| Ads and Sponsored Content | Yes | No |
| Intent Understanding | Moderate (keyword focused) | High (context + natural language) |
| Personalized Response | No (general links) | Yes (tailored natural-language output) |
Both Google and ChatGPT are powerful. But they're built differently.
Google finds the now. ChatGPT explains the why. Google shows you options. ChatGPT gives you answers.
If you're a business, understanding these systems helps you tailor your content better—especially if you're wondering why your site is visible on Google but not mentioned in a ChatGPT response.
Need help getting your brand seen in both worlds? Qaushik Labs helps businesses optimize for both search engines and AI platforms.
No, ChatGPT doesn't use traditional SEO ranking factors like backlinks or page speed. Instead, it relies on source weightage from its training data and internal knowledge patterns. When web browsing is enabled, it may use some relevance signals but not the full Google algorithm.
ChatGPT primarily uses pre-trained knowledge up to its cutoff date. If your content wasn't indexed during training or lacks cross-source validation, it may not appear in responses. For live searches, newer content has a better chance of inclusion.
Focus on getting mentions across multiple platforms (directories, forums, news sites), use structured data markup, create authoritative content that gets referenced by others, and ensure your information is consistent across different sources.
For local queries, structured directories like Yelp and specialized platforms get high weightage (25-35%). For general information, official websites and cross-verified sources are prioritized. Social media profiles typically get the lowest weightage.
Only when web browsing tools are enabled (Pro users or specific configurations). By default, ChatGPT relies on its training data cutoff and doesn't access real-time information like current prices, breaking news, or live business hours.